Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and cryptocurrencies are two distinct forms of digital money that have garnered significant attention in recent years. Both represent a shift away from traditional physical currencies to digital alternatives, but they differ fundamentally in their design, purpose, and regulatory frameworks. Understanding the differences between CBDCs and cryptocurrencies is crucial for comprehending the future landscape of digital finance. This article explores these differences in detail, highlighting their unique characteristics and implications for the financial system.
1. Definition and Purpose
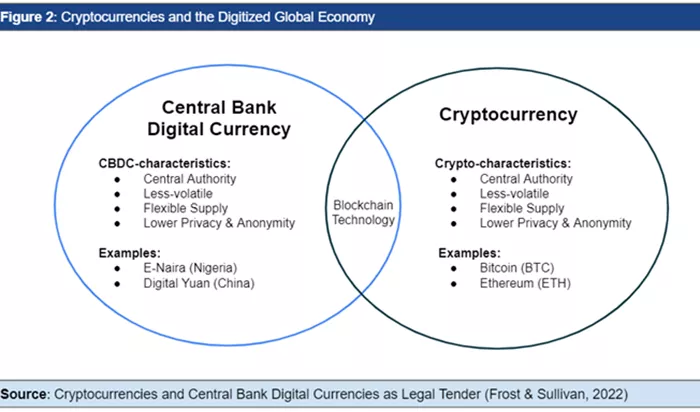
CBDC
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are digital forms of a country’s official currency issued and regulated by the central bank. They are intended to serve as a legal tender and a direct substitute for physical cash. The primary purpose of CBDCs is to enhance the efficiency of the monetary system, provide a secure and stable form of digital money, and potentially address issues related to financial inclusion and payment system resilience.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies are digital or virtual currencies that use cryptographic techniques for secure transactions and control of new units. Unlike CBDCs, cryptocurrencies are typically decentralized and operate on blockchain technology—a distributed ledger maintained by a network of computers. The purpose of cryptocurrencies varies, from serving as an investment asset to facilitating transactions in a decentralized manner, often bypassing traditional financial intermediaries.
2. Regulation and Control
CBDC
CBDCs are issued and regulated by central banks, which means they are subject to the country’s monetary policies and regulatory framework. Central banks have full control over the issuance, supply, and stability of CBDCs, ensuring they align with national economic objectives. CBDCs are designed to be stable, with their value pegged to the country’s fiat currency, and are backed by the central bank’s authority.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies are typically decentralized and operate independently of any central authority. While some cryptocurrencies may adhere to regulations, they are not controlled or issued by any central bank or government. The decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies means that their value can be highly volatile, and they are not backed by any physical asset or government guarantee.
See also: Everything You Need To Know About Cryptocurrency: What Is It?
3. Technology and Infrastructure
CBDC
CBDCs can be built using various technologies, including distributed ledger technology (DLT) or centralized databases. The choice of technology depends on the central bank’s objectives and requirements. CBDCs are often designed to integrate seamlessly with existing financial infrastructure, providing a stable and secure means of digital payment that can be easily adopted by businesses and consumers.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies rely predominantly on blockchain technology, which is a form of DLT that records transactions across a distributed network of nodes. This decentralized approach ensures transparency and security but can also lead to scalability issues. Cryptocurrencies operate on a peer-to-peer network, where transactions are validated by network participants through consensus mechanisms such as proof of work or proof of stake.
4. Privacy and Anonymity
CBDC
The level of privacy associated with CBDCs varies depending on the design chosen by the central bank. While CBDCs offer privacy features similar to traditional cash, they may also incorporate mechanisms for tracking and monitoring transactions to prevent illicit activities and ensure regulatory compliance. The balance between privacy and transparency is a key consideration in the design of CBDCs.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies offer varying degrees of privacy and anonymity. While transactions in some cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are pseudonymous (meaning the identities behind transactions are not directly visible but can be traced through addresses), others, like Monero or Zcash, are designed to enhance user privacy and provide greater anonymity. The degree of privacy depends on the cryptocurrency’s design and the specific privacy features it employs.
5. Economic and Financial Implications
CBDC
CBDCs have the potential to reshape the financial system by offering a more efficient and inclusive payment system. They can reduce transaction costs, enhance financial inclusion by providing access to digital financial services, and improve the effectiveness of monetary policy. However, they also raise concerns about the potential impact on the traditional banking sector and the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies have introduced new paradigms in finance, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) and smart contracts. They offer alternative investment opportunities and enable peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries. However, their volatility, regulatory uncertainty, and potential use in illicit activities pose challenges. The rise of cryptocurrencies has prompted discussions about their impact on financial stability and the need for regulatory frameworks.
Conclusion
While both CBDCs and cryptocurrencies represent advancements in digital money, they differ significantly in their design, purpose, and regulatory frameworks. CBDCs are centralized, government-issued digital currencies aimed at enhancing the efficiency of the monetary system and ensuring stability. In contrast, cryptocurrencies are decentralized digital assets that operate independently of central authorities, offering varied uses and levels of privacy. Understanding these differences is essential for navigating the evolving landscape of digital finance and assessing the implications for the future of money and payments.
Related Topics: